Work in Progress
This is a work in progress and is not ready to be published yet.
The integration of Holochain, hREA/ValueFlows, and Cardano offers a groundbreaking approach for Open Value Networks (OVNs) engaged in peer production, particularly within the context of open-source, Do-It-Yourself (DIY) projects like PEP Master. By combining Holochain’s decentralized contribution tracking, hREA/ValueFlows’ economic modeling, and Cardano’s robust blockchain infrastructure, this hybrid model enables distributed fabrication, secure asset tokenization, and regulatory compliance for collaboratively produced therapeutic devices. This article explores how these technologies converge to support OVNs, with a specific focus on the PEP Master project, its objectives, and the current implementation plan, as illustrated in the accompanying diagram.
- Open Value Networks are a type of peer production network that are characterized by their focus on value distribution and the use of blockchain technology to support their operations.
- Holochain offers an agent-centric architecture that aligns with self-sovereignty and peer-to-peer collaboration, allowing participants to maintain control over their data while contributing to a shared network.
- hREA/ValueFlows provides a standardized vocabulary for tracking economic activities (Resources, Events, Agents), ensuring transparent and auditable records of contributions and value flows.
- Cardano brings a secure blockchain layer for tokenization, certification, and economic incentives, supporting distributed ownership and global accessibility through its smart contract capabilities.
This synergy creates a robust ecosystem for OVNs, enabling them to manage complex workflows, reward contributors fairly, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards—a critical requirement for projects like PEP Master.
Core OVN Principles and the Role of Technology
Open Value Networks operate on principles that recognize value as a complex, triadic relationship between valuables (realities), tokens (symbolic representations), and valuations (both subjective experiences and inter-subjective shared meanings). Unlike traditional economic models that treat value as a tangible commodity that can be created, stored, or transferred, OVNs understand that value fundamentally rests on “subjective experiences that move human beings into action”. This perspective avoids value fetishism and shapes how technology is employed within the network.
OVNs also embrace a more complex approach to ownership, recognizing multiple forms of property relations including private, shared, commons, and notably, “nondominium” - assets that by their nature cannot be owned. For instance, while individual components of the network may be privately owned or held in commons, the network’s emergent capabilities often exist as nondominium, similar to how the Bitcoin network itself transcends traditional ownership models.
Openness and Transparency
OVNs prioritize open access to information, processes, and decision-making. This transparency extends to contribution tracking, resources flows, and governance, ensuring that all participants can audit and verify activities. Holochain’s distributed hash table (DHT) and hREA/ValueFlows’ transparent logging of economic events (Resources, Events, Agents) support this principle by providing auditable records of all interactions within the network.
Nondominium and Diverse Property Regimes
OVNs embrace a variety of property regimes, including private, shared, commons, and public, but they also introduce the concept of nondominium—assets that, by their nature, cannot be owned or controlled. For example, the Bitcoin Network operates as a nondominium: it exists as an aggregated entity providing token exchange services, but if any individual or group gains enough influence to control it, the network dissipates due to loss of trust. In contrast, mining computers are privately owned, and the Bitcoin code exists as a commons. Cardano’s blockchain complements this by tokenizing assets (e.g., NFTs for certified designs) that can exist under various property regimes, while Holochain ensures that the network itself remains a nondominium, fostering trust and decentralization.
Meritocratic Governance
Access to decision-making in OVNs is based on contributions rather than hierarchical power structures. Holochain’s agent-centric architecture supports this by accurately tracking individual contributions via hREA/ValueFlows, ensuring that influence is distributed based on merit. Cardano’s smart contracts further enable merit-based reward systems, linking contributions to token rewards.
Value as a Triadic Relation
OVNs redefine value as a triadic relation between a valuable (a reality), a token (a symbol, which may or may not be monetary), and a valuation (a subjective and inter-subjective experience shaped by culture and socialization). Value is not a thing that can be created, stored, or transferred; rather, it emerges from subjective experiences that move individuals to action. This perspective avoids value fetishism and emphasizes the relational nature of economic interactions. hREA/ValueFlows captures this by modeling economic events and processes as relational flows, while Cardano’s token reward system provides symbolic tokens that reflect these valuations, ensuring rewards align with the subjective and inter-subjective value perceived by the network.
Modularity and Interoperability
OVNs embrace modular designs and interoperable systems to ensure flexibility and scalability. Holochain’s customizable application framework supports this by allowing tailored solutions for specific use cases, while Cardano’s interoperability with decentralized storage solutions like Iagon ensures seamless integration with other systems.
Holochain’s modular architecture, built on Zomes and DNA, provides core composability features that integrate with Moss and Neighborhood as building blocks for collaboration and social sensemaking. This architectural approach enables flexible and adaptable solutions for different use cases.
Cardano complements this modularity through its cross-chain and cross-platform interoperability capabilities. A future Cardano Zome will enable direct integration with Holochain, while Cardano’s native interoperability with other blockchains (demonstrated through BitcoinOS and FluidToken) leverages the robustness of its EUTXO transaction model and the Inter-Blockchain-Protocol (IBP).
Global Accessibility
OVNs aim to create networks that transcend geographical boundaries through a “glocal” (global + local) approach. Cardano’s blockchain enables transactional global interoperability via its smart-contracts system, while Holochain provides local context and governance through its agent-centric architecture. This hybrid model allows contributors to transport their credentials and reputation across different OVNs seamlessly.
The integration of Holochain with ADAM (https://coasys.org/adam) establishes a common language and perspective for translating local credentials, while Cardano secures the cross-network transaction of these credentials and reputations. ADAM’s meta-ontology, which defines three classes (Agents, Languages, and Perspectives), creates a spanning layer that enables many-to-many mappings between user interfaces and existing web technologies. This architecture allows for private, locally stored graph databases that associate data across different Languages while maintaining global interoperability.
Sustainability
OVNs prioritize environmentally and economically sustainable practices. Holochain’s energy-efficient architecture aligns with this principle by minimizing the environmental impact of peer production networks, while Cardano’s Ouroboros Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism ensures long-term sustainability through a more energy-efficient consensus mechanism than Proof-of-Work (PoW) or other PoS mechanisms used by other blockchains.
Holochain’s agent-centric architecture fundamentally differs from traditional blockchain approaches by eliminating the need for global consensus. Instead of all nodes processing all transactions, each agent maintains their own local chain and only validates the data they need. This distributed validation approach dramatically reduces computational overhead and energy consumption. The system scales linearly with the number of users, rather than exponentially like traditional blockchains, making it inherently more energy-efficient.
Cardano’s Ouroboros protocol represents a significant advancement in sustainable blockchain technology. Unlike energy-intensive Proof-of-Work systems, Ouroboros achieves the same security guarantees while consuming only a fraction of the energy. Research indicates that Cardano’s energy consumption is approximately 0.01% of Bitcoin’s, using about 6 GWh annually compared to Bitcoin’s 110.53 TWh. This efficiency is achieved through:
- Stake-based validator selection instead of computational puzzles
- Deterministic block creation process
- Efficient network communication protocols
- Optimized transaction validation
The combination of Holochain’s agent-centric architecture and Cardano’s Ouroboros protocol creates a highly sustainable infrastructure for OVNs, enabling them to scale their operations without compromising environmental responsibility.
Peer-to-Peer Collaboration
OVNs emphasize direct interactions between participants, reducing reliance on intermediaries. Holochain’s peer-to-peer networking capabilities enable real-time collaboration, while Cardano ensures secure and transparent transactions without centralized control.
Continuous Innovation
OVNs model is in continuous improvment/evolution, iteratively improving through the current societal and technological transitions. Holochain, by it’s lack of censensus mechanisme bring the necessary flexiblity for the OVNs model to evolve and experiment in pararel in different economic contexte like a living economic-lab. Cardano, bring the transactional backbone with its structured data and financial architecture. It’s a global security that allow local experimentations with HOlochain communities. It’s the perfect hybridation between data and agent centricity.
Each OVN can have its own local economic model, enable by Holochain and hREA/Valueflows and then the global Cardano smart contract architecture can make the connection and validation at a global level.
ADAM (https://coasys.org/adam) could be a bridge between the OVNs and the Cardano smart-contracts. It’s a meta-ontology defining 3 classes: Agents, Languages and Perspectives. These form a spanning-layer that enables many-to-many mappings between user-interfaces (i.e. apps) and existing web technologies wrapped in “Languages”. Apps interface with “Perspectives” which are private and locally stored graph databases associating data across different Languages.
Global Accessibility
OVNs aim to create networks that transcend geographical boundaries. Cardano’s blockchain enables transactional global interoperability via its smart-contracts system, while Holochain provide the local context and governance via it’s agent-centric architecture. It’s a mix between local and global (Glocal). Contributors to a local OVN can transport their credentials and reputation to facilitate their access to other OVNs.
Holochain + ADAM favorize the translations of those local credential by establishing a common language/perspective while Cardano secure the transactions of theses credetentials and reputations across the local networks.
Self-Sovereignty
OVNs respect the autonomy of individual contributors, allowing them to maintain control over their data and contributions. Holochain’s agent-centric design ensures that participants retain sovereignty over their personal data, while Cardano’s decentralized identity (DID) zone supports secure and self-sovereign identity management.
By adhering to these principles, OVNs create ecosystems that foster collaboration, innovation, and equitable economic interactions. The integration of Holochain, hREA/ValueFlows, and Cardano provides a technical foundation that not only supports but also amplifies these principles, enabling OVNs to operate effectively in contexts like the PEP Master project, where transparency, fairness, and regulatory compliance are critical.
The PEP Master Context
PEP Master is an open-source DIY therapeutic device and game developed by a consortium involving Sensorica, Sainte Justine Hospital, Breathing Games and Ludociels. The project aims to increase accessibility to medical and therapeutic equipment by leveraging peer production and Web3 technologies. The primary objectives include:
- Achieving ISO standards for the PEP Master device.
- Validating the clinical relevance of peer-produced PEP Master devices through medical research.
- Establishing validation and certification methods for device blueprints and fabrication processes.
- Implementing secure medical data storage and transfer mechanisms.
- Engaging with governmental agencies like Health Canada for regulatory approval.
The PEP Master project operates within a niche where quality, safety, and regulatory compliance are paramount. Traditional economic models often fail to effectively address rare medical conditions. To overcome this limitation, the PEP Master project implements a trust-based economic model that leverages open collaboration and distributed fabrication. This approach increases accessibility to medical devices, making it particularly valuable for addressing marginalized or niche rare medical conditions.
The hREA/ValueFlows Framework
hREA (Holochain Resource-Event-Agent) implements the ValueFlows specification, a standardized vocabulary for describing economic activities in decentralized networks. This framework is central to the PEP Master project, as it enables transparent tracking of contributions and value flows across the distributed fabrication network. The framework consists of several key components:
Core Components
-
Economic Agents: Participants in the network, such as:
- Engineers and designers contributing device blueprints
- Medical professionals validating designs
- Fabricators producing devices
- Patients providing feedback and usage data
- Organizations like hospitals and makerspaces
-
Economic Events: Tracked activities that represent value flows:
- Design submissions and iterations
- Validation and certification processes
- Fabrication and assembly steps
- Quality control checks
- Device deployment and usage
- Maintenance and support activities
-
Economic Resources: Tangible and intangible assets:
- Device blueprints and documentation
- Physical components and materials
- Assembled PEP Master devices
- Certifications and validations
- Usage data and feedback
- Knowledge and expertise
Process Flows
hREA/ValueFlows models the PEP Master workflow as interconnected processes:
-
Design Process:
- Input: Engineering expertise, medical requirements
- Activities: Design creation, review, iteration
- Output: Validated device blueprints
-
Certification Process:
- Input: Device blueprints, regulatory standards
- Activities: Testing, validation, documentation
- Output: Certified designs, compliance records
-
Fabrication Process:
- Input: Certified blueprints, materials
- Activities: Component production, assembly, testing
- Output: Functional PEP Master devices
-
Distribution Process:
- Input: Verified devices, user requirements
- Activities: Deployment, training, support
- Output: Installed and operational devices
Value Tracking and Distribution
The framework enables:
- Transparent Contribution Tracking: Every contribution, from design improvements to quality testing, is recorded and linked to specific outcomes
- Multi-dimensional Value Assessment: Captures both tangible (e.g., components, labor) and intangible (e.g., knowledge, innovation) value contributions
- Fair Reward Distribution: Enables merit-based compensation through:
- Direct value flow tracking
- Contribution verification
- Automated reward distribution via Cardano smart contracts
Integration Benefits
The hREA/ValueFlows framework provides several advantages for the PEP Master project:
- Regulatory Compliance: Maintains detailed audit trails of all design, validation, and fabrication processes
- Quality Assurance: Tracks and verifies each step in the device production workflow
- Knowledge Management: Captures and preserves expertise and improvements across the network
- Trust Building: Creates transparency and accountability in the peer production process
- Scalability: Enables consistent processes across different fabrication locations while maintaining local autonomy
This comprehensive framework ensures that every contribution to the PEP Master project is properly tracked, validated, and rewarded, while maintaining the high standards required for medical device production.
Holochain’s Role in Decentralized Collaboration
Holochain provides the foundational infrastructure for the PEP Master project, enabling secure, scalable, and agent-centric collaboration. Its architecture is specifically designed to support distributed peer production while maintaining data integrity and privacy requirements essential for medical devices.
Core Architectural Features
Agent-Centric Design
- Personal Source Chains: Each participant maintains their own cryptographic chain of actions
- Sovereign Data Control: Users retain ownership and control of their personal data
- Local Validation: Actions are validated against shared rules before being committed
- Flexible Identity Management: Supports multiple identity contexts and credentials
Distributed Hash Table (DHT)
- Secure Data Storage: Tamper-resistant storage of design data and documentation
- Selective Redundancy: Data is replicated across multiple nodes for reliability
- Privacy Zones: Private DHT spaces for sensitive medical and patient information
- Content-Addressable: Efficient retrieval and verification of stored information
Peer-to-Peer Networking
- Direct Communication: Enables real-time collaboration between participants
- Network Resilience: Functions without central servers or coordination
- Scalable Architecture: Performance improves with network growth
- Efficient Data Propagation: Optimized for large-scale distributed systems
Application in PEP Master
Design Collaboration
-
Blueprint Management:
- Secure storage of device designs
- Version control and change tracking
- Collaborative design iterations
- Integration with CAD tools
-
Validation Workflow:
- Medical professional review process
- Regulatory compliance checking
- Design feedback loops
- Documentation management
Fabrication Coordination
-
Distributed Manufacturing:
- Coordination between fabrication sites
- Quality control protocols
- Component tracking
- Assembly verification
-
Supply Chain Management:
- Material sourcing and tracking
- Inventory management
- Production scheduling
- Distribution coordination
Data Management
-
Medical Data Handling:
- Private DHT zones for patient data
- HIPAA-compliant storage
- Secure access controls
- Audit trail maintenance
-
Usage Analytics:
- Anonymous usage statistics
- Performance monitoring
- Safety tracking
- Outcome analysis
Technical Implementation
Zome Architecture
- Modular Components: Specialized functions for different aspects of the project
- Composable Design: Mix and match capabilities as needed
- Extensible Framework: Easy addition of new features
- Secure Boundaries: Isolation between different functional areas
Integration Points
-
hREA/ValueFlows:
- Economic activity tracking
- Contribution validation
- Value flow mapping
- Reward distribution
-
Cardano Bridge:
- Certification recording
- Token management
- Global state synchronization
- Cross-chain transactions
Performance and Scalability
Real-Time Collaboration
- Instant Updates: Local changes are immediately visible
- Fast Synchronization: Efficient peer-to-peer data propagation
- Conflict Resolution: Automatic handling of concurrent modifications
- Offline Support: Continue working without network connection
Resource Efficiency
- Minimal Hardware Requirements: Runs on standard consumer hardware
- Optimized Storage: Smart data replication strategies
- Bandwidth Efficient: Only transmit necessary data
- Energy Conscious: No wasteful consensus mechanisms
This infrastructure enables PEP Master to operate as a truly distributed, collaborative network while maintaining the high standards required for medical device development and production. The combination of Holochain’s agent-centric architecture with its robust data integrity mechanisms creates a foundation that is both scalable and secure, essential for the project’s success.
ADAM: A Bridge Between Holochain and Cardano
The Agent-centric Distributed Application Meta-Ontology (ADAM) can serve as a powerful integration layer between Holochain and Cardano in the PEP Master project. ADAM’s architecture provides a meta-ontology that enables seamless interaction between different decentralized technologies while maintaining the benefits of each system.
Core ADAM Components
-
Agents:
- Represented by Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
- Can maintain identities across both Holochain and Cardano networks
- Enable consistent identity management for contributors, validators, and users
- Support signed expressions for verifiable contributions
-
Languages:
- Bridge different technological contexts
- Wrap Holochain DNAs and Cardano smart contracts
- Enable cross-platform data translation
- Facilitate protocol-agnostic interactions
-
Perspectives:
- Private, locally stored graph databases
- Connect data across different technological contexts
- Enable personal data sovereignty
- Support collaborative spaces through shared perspectives
Integration Benefits
-
Technological Bridging:
- Seamless interaction between Holochain’s agent-centric and Cardano’s blockchain architectures
- Unified interface for developers and users
- Consistent data representation across platforms
- Simplified cross-platform development
-
Social Coordination:
- Creation of shared Neighborhoods for collaborative device development
- Social DNA for encoding community practices and standards
- Evolving governance models for OVN operations
- Adaptive social systems for different stakeholder groups
-
Enhanced Interoperability:
- Common semantic layer for all interactions
- Unified credential and reputation systems
- Consistent data models across platforms
- Seamless value flow tracking
Practical Applications in PEP Master
-
Design Collaboration:
- Shared perspectives for design teams
- Cross-platform version control
- Integrated feedback mechanisms
- Collaborative validation workflows
-
Certification Process:
- Unified credential verification
- Cross-platform regulatory compliance
- Integrated audit trails
- Seamless certification workflows
-
Value Distribution:
- Integrated contribution tracking
- Cross-platform reward distribution
- Unified reputation systems
- Transparent value flows
By incorporating ADAM, the PEP Master project can create a more cohesive and user-friendly experience while maintaining the technical advantages of both Holochain and Cardano. This integration layer simplifies development, enhances collaboration, and ensures seamless operation across different technological contexts.
Cardano’s Role in Certification and Tokenization
Cardano serves as the backbone for certification, tokenization, and economic incentives in the PEP Master project. Its proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, robust smart contract platform, and native token capabilities provide essential features for ensuring regulatory compliance and sustainable value distribution.
Certification Infrastructure
-
NFT-Based Certification (CIP-25/68):
- Unique digital certificates for validated designs
- Immutable proof of validation and compliance
- Traceable certification history
- Integration with regulatory frameworks
- Support for multiple certification levels
-
Smart Contract Validation:
- Automated certification workflows using Aiken
- Multi-signature approval processes
- Regulatory compliance checks
- Version control and design iteration tracking
- Automated compliance reporting
-
Decentralized Storage Integration:
- Iagon integration for distributed storage
- Redundant backup of certification data
- Secure access control mechanisms
- HIPAA-compliant data management
- Long-term archival capabilities
Economic Incentive System
-
Token Architecture:
- Native tokens for contribution rewards
- Utility tokens for network access
- Governance tokens for decision-making
- Staking mechanisms for long-term alignment
- Dynamic reward distribution models
-
Value Distribution:
- Merit-based reward allocation
- Automated payment distribution
- Transparent contribution tracking
- Multi-currency support
- Cross-border payment solutions
-
Staking and Governance:
- Stake-based voting rights
- Proposal submission mechanisms
- Community-driven parameter adjustments
- Risk mitigation through staking
- Decentralized governance protocols
Technical Implementation
-
Smart Contract Development:
// Example certification validator validator { fn certify_design( ctx: ScriptContext, validator_signatures: Vec<PubKeyHash>, design_hash: Hash, certification_level: Int, ) -> Bool { // Validation logic verify_signatures(validator_signatures) && verify_design_hash(design_hash) && verify_certification_requirements(certification_level) } } -
Token Standards:
- Implementation of CIP-25/68 for NFT minting
- Custom token policies for different use cases
- Metadata standards for certification
- Interoperability with other blockchain systems
- Upgradeable token contracts
-
Integration Points:
- Holochain bridge for data validation
- ADAM integration for cross-platform compatibility
- External oracle connections
- Regulatory reporting interfaces
- Third-party audit support
Security and Compliance
-
Regulatory Framework:
- Compliance with medical device regulations
- HIPAA compliance for patient data
- ISO standard adherence
- Audit trail maintenance
- Regular compliance reporting
-
Security Measures:
- Multi-signature requirements
- Time-locked transactions
- Hardware security module support
- Formal verification of critical contracts
- Regular security audits
-
Risk Management:
- Failsafe mechanisms
- Emergency pause functionality
- Gradual upgrade paths
- Backup and recovery procedures
- Insurance coverage options
Future Developments
-
Scalability Improvements:
- Hydra layer-2 integration
- Parallel certification processing
- Optimized storage solutions
- Enhanced throughput capabilities
- Cross-chain interoperability
-
Enhanced Features:
- Advanced tokenomics models
- AI-assisted validation
- Automated compliance checking
- Real-time reporting dashboards
- Predictive analytics integration
-
Ecosystem Growth:
- Partner network expansion
- Cross-platform integrations
- Developer tool improvements
- Community governance enhancement
- Educational resource development
This comprehensive integration of Cardano’s capabilities ensures that the PEP Master project maintains high standards of security, compliance, and economic sustainability while fostering innovation and collaboration within the open-source medical device community.
The Hybrid Model: Holochain + Cardano in Action
The integration of Holochain and Cardano creates a hybrid model that leverages the strengths of both technologies to support the PEP Master workflow. The process is illustrated in the following diagram:
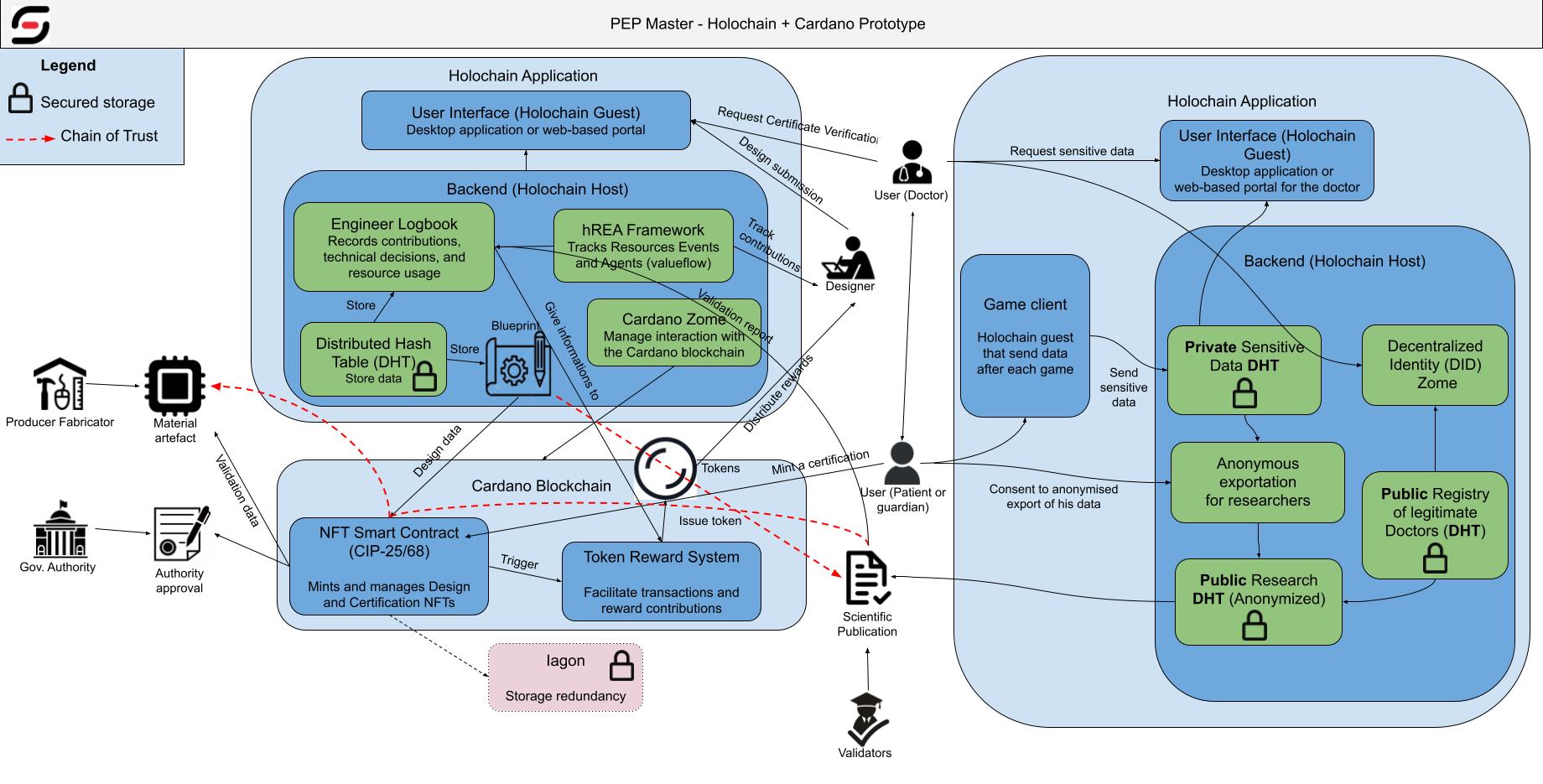
The diagram outlines the following steps:
- Design Submission and Contribution Logging (Holochain): Engineers and designers submit designs through the Holochain application, where contributions are logged using hREA/ValueFlows. The backend stores design data in a distributed hash table (DHT) for transparency.
- Validation Process (Holochain + Cardano): Validators (e.g., doctors) review designs on Holochain, and once validated, the process triggers Cardano to mint an NFT for certification.
- Certification Process (Cardano): Cardano’s smart contracts manage the certification, creating an NFT (using CIP-25/68 standards) that represents the validated design, ensuring legal recognition.
- Fabrication and Distribution (Holochain + Cardano): The certified design is sent to fabricators (e.g., makerspaces), with Cardano managing the chain of trust for material artifacts.
- Therapeutic Use and Data Management (Holochain): Patients use the PEP Master device, and game clients report sensitive data (e.g., health outcomes) to a private DHT zone on Holochain, ensuring privacy.
- Research Export (Holochain): Anonymized data is exported for public research, maintaining compliance with privacy regulations.
- Token Reward System (Cardano): Contributors receive tokens based on their logged contributions, incentivizing participation and sustaining the network.
- Forking and Iteration (Holochain): Designs can be forked and remixed on Holochain, fostering continuous innovation.
This hybrid model ensures that PEP Master achieves its goals of transparency, regulatory compliance, and fair value distribution while fostering a sustainable peer production ecosystem.
Current Plan and Next Steps
The PEP Master project is currently in the prototyping phase, with the following milestones:
- Prototype Development: The team is building a functional prototype integrating Holochain and Cardano, as outlined in the diagram. This includes the user interface for doctors and patients, the backend for contribution tracking, and Cardano’s smart contracts for certification and rewards.
- Regulatory Engagement: The consortium is engaging with Health Canada to secure regulatory approval, using the hybrid model to demonstrate compliance with ISO standards and safety requirements.
- Data Storage and Privacy: The project is implementing a data storage prototype using Holochain’s DHT and Cardano’s Iagon integration, ensuring secure handling of sensitive patient data.
- Community Building: Sensorica and its partners are fostering a community of contributors, including engineers, doctors, and patients, to participate in the OVN and refine the PEP Master device through iterative design.
The next steps include testing the prototype in a real-world setting at Sainte Justine Hospital, gathering feedback from patients and doctors, and iterating on the design. The team also plans to expand the token reward system to attract more contributors, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the project.
Future Outlook
The integration of Holochain, hREA/ValueFlows, and Cardano offers a transformative framework for Open Value Networks like PEP Master. By combining Holochain’s scalable, agent-centric architecture with hREA/ValueFlows’ transparent economic modeling and Cardano’s secure blockchain capabilities, the project creates a comprehensive ecosystem for peer production. This model not only addresses the challenges of quality, safety, and regulatory compliance in medical device production but also paves the way for a self-sustaining p2p economy.
As the PEP Master project progresses, it has the potential to set a precedent for other peer-produced medical devices, demonstrating how Web3 technologies can empower communities to innovate, collaborate, and create value equitably. The hybrid model of Holochain and Cardano could inspire broader adoption of OVN principles, fostering resilient and sustainable economic systems that prioritize cooperation and shared value creation in the digital age.